Transformer
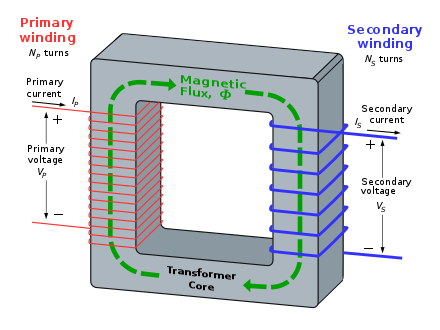
A transformer is a device that transfers electric energy from one alternating-current circuit to one or more other circuits, either increasing (stepping up) or reducing (stepping down) the voltage. A transformer is an electrical device that trades voltage for current in a circuit, while not affecting the total electrical power. This means it takes high-voltage electricity with a small current and changes it into low-voltage electricity with a large current, or vice versa. A transformer is a static device which can transfer power from one circuit to another at same frequency.
A transformer is defined as a passive electrical device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through the process of electromagnetic induction. It is most commonly used to increase ('step up') or decrease ('step down') voltage levels between circuits. Transformers are rated in kVA because the losses occurring in the transformers are independent of power factor. KVA is the unit of apparent power. It is a combination of real power and reactive power. Transformers are manufactured without considering the load being connected. A transformer consists of two electrically isolated coils and operates on Faraday's principal of “mutual induction”, in which an EMF is induced in the transformers secondary coil by the magnetic flux generated by the voltages and currents flowing in the primary coil winding.
